huwangbei2019_Crypto1
huwangbei2019_Crypto¶
Just decrypt it.
Examination Site¶
- RSA
- multiplicative group modulo N
Analysis¶
The key code:
def gen(): while True: g = getPrime(500) a = b = 0 while not gmpy2.is_prime(2*g*a+1): a = random.randint(2**523, 2**524) while not gmpy2.is_prime(2*g*b+1): b = random.randint(2**523, 2**524) h = 2*g*a*b+a+b if gmpy2.is_prime(h): p = 2*g*a+1 q = 2*g*b+1 return p*q, g
Reference:
Further Attacks On Server-Aided Rsa Cryptosystems
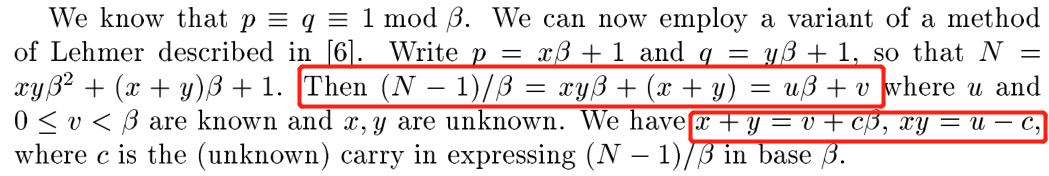
According to the article, we can fristly calculate the a*b and (a+b).
As we have known N and g,we can calculate the u and v:
h = (N-1)/(g) u = h/(g) # 4 * xy v = h%(g) # 2 * (x+y)
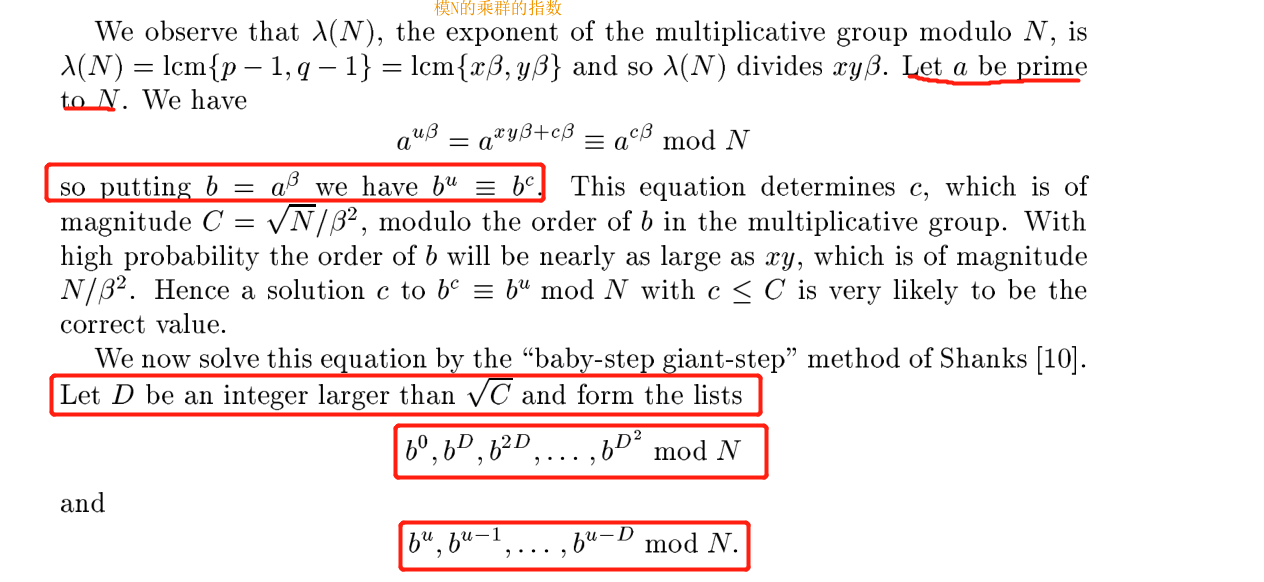

The article gives us a algorithm:Find a D being an integer larger than sqrt(C) and form the lists b0,bD,b2D,……,bD*D mod N and bu,bu-1,……,b^u-D we can sort these lists and find a common value b^rD ≡ b^u-D mod N and the c is rD+s!
Exploit¶
#encoding:utf-8 from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long,long_to_bytes from gmpy2 import * # N = pq 2050bit; p 1025 bit; q 1025 bit N = 67962725468240199924103144864951334845750492508509360358636648068909779932072313362607631417524914992411826230276465100489023746209605790020210412575433464887238013738989770872867041592441153421617243161413094177629581581728221687772551567927241071007480087793370382177952900925657974338348428988433092737432689512506966089398873760401212521089061934975582692308605433023613521500237258699626587149952370997420510392932840377408736864097301789914658244266522930092113493152991783027162871212338968297436073316959569822974289536559300512091342692975133379473145882007983357289924135373382264527866381118893476257705939L # g 500bit; is p-1 and q-1 prime factor # p = 2*g*a + 1;p = 2*g*b + 1 g = 3235645591686044532495326878291617484542045511433360748778013933565021819649890342389737893735574764418484922895778834144345295691799766302763199373647L e = 65537 C = 7918937034819399210460701361082120267249016865135589044938397478179178418982216265766430882604707450651405790878761026681351233717846491757101684210544361607883043938000941498442897699091016071609425252346011280078699567193949155766516051130050592046343488075564740812480634431357869210712013396437065989799117830247228129120071415956115563715118301273810713118159274551107354918579047901176471910532333125717712607469726900731370186233984133546278420585661042017307325998441634272568791745798269084955686428143476025911093137683806174746625559312685862694783475952178855060639359433340135424849663386199035593137765L h = (N-1)/(g) u = h/(g) v = h%(g) def Solve_c(): sqrt_N = iroot(mpz(N),2)[0] C = div(sqrt_N,pow(g,2)) a = 2 b = powmod(a,g,N) for i in range(2,C): D = (iroot(C,2)[0] + 1) * i final = powmod(b,u,N) for r in range(D): print r*D for s in range(D): if powmod(b,r*D+s,N) == final: print "r =",r,"s =",s,"i =",i #r = 5168 s = 2145 i = 2 return r * D + s c = Solve_c() print "c:",c # c = 51589121 A = u - c # x * y = u - c B = v + c*g # x + y = v + c*g delta = iroot((B*B-4*A),2)[0] x = (B+delta)/2 y = (B-delta)/2 a = x/2 b = y/2 p = 2*g*a + 1 q = 2*g*b + 1 d = invert(e,(p-1)*(q-1)) m = powmod(C,d,N) print long_to_bytes(m) #flag{bf82d1cd-67b1-42bd-a7b5-f119f0246dfe}